How to Check if Your Website is Indexed by Google
Use the site: operator to instantly see if Google and Bing can find your website - no tools required
Want to know if your website shows up in Google search results? There’s a simple way to check that takes under 2 minutes and doesn’t require any special tools or accounts.
The fastest method uses a search operator called site: that tells Google and Bing to show only results from your specific website.
The Quick Check: Using site:yourwebsite.com
On Google
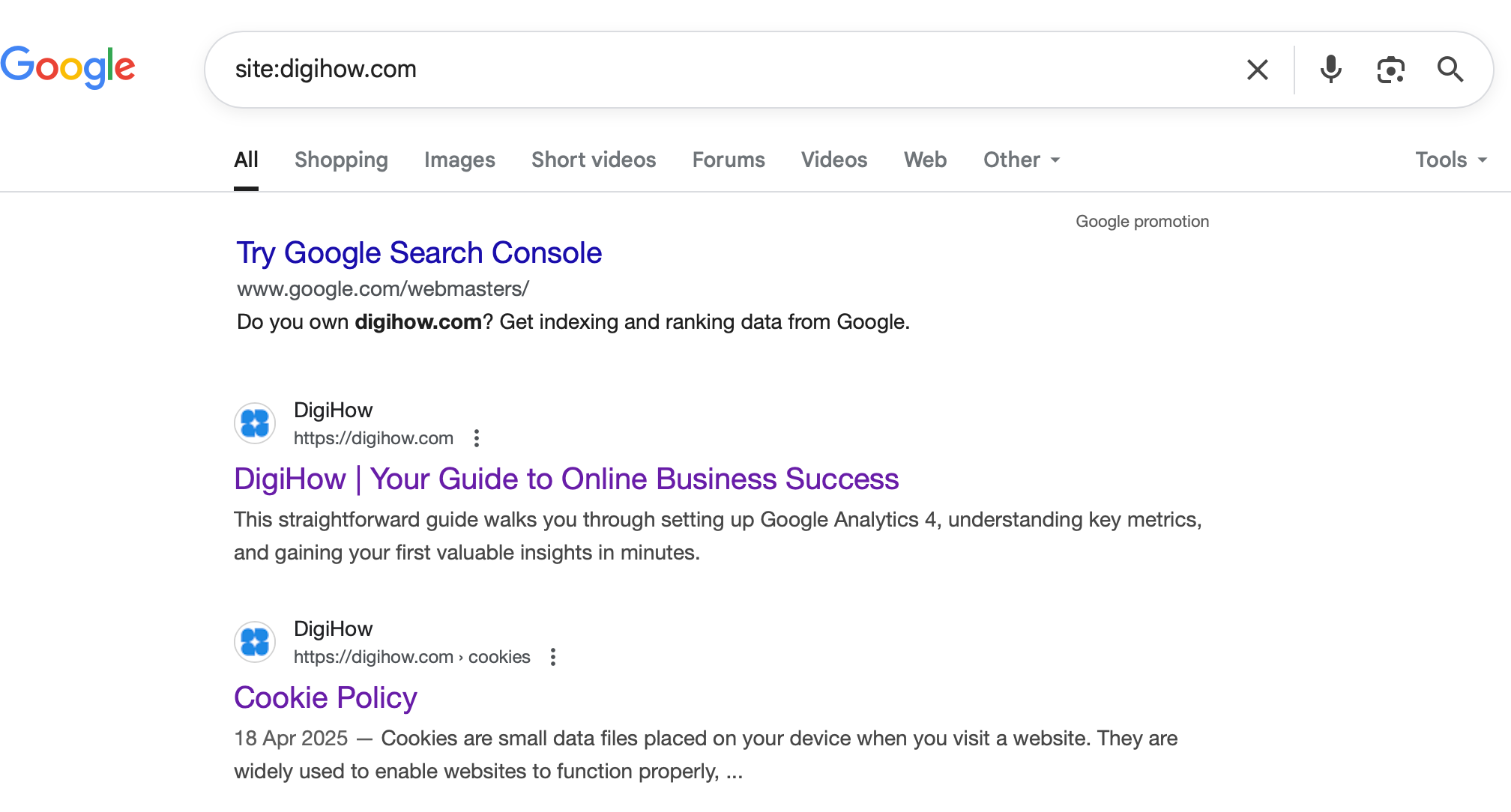
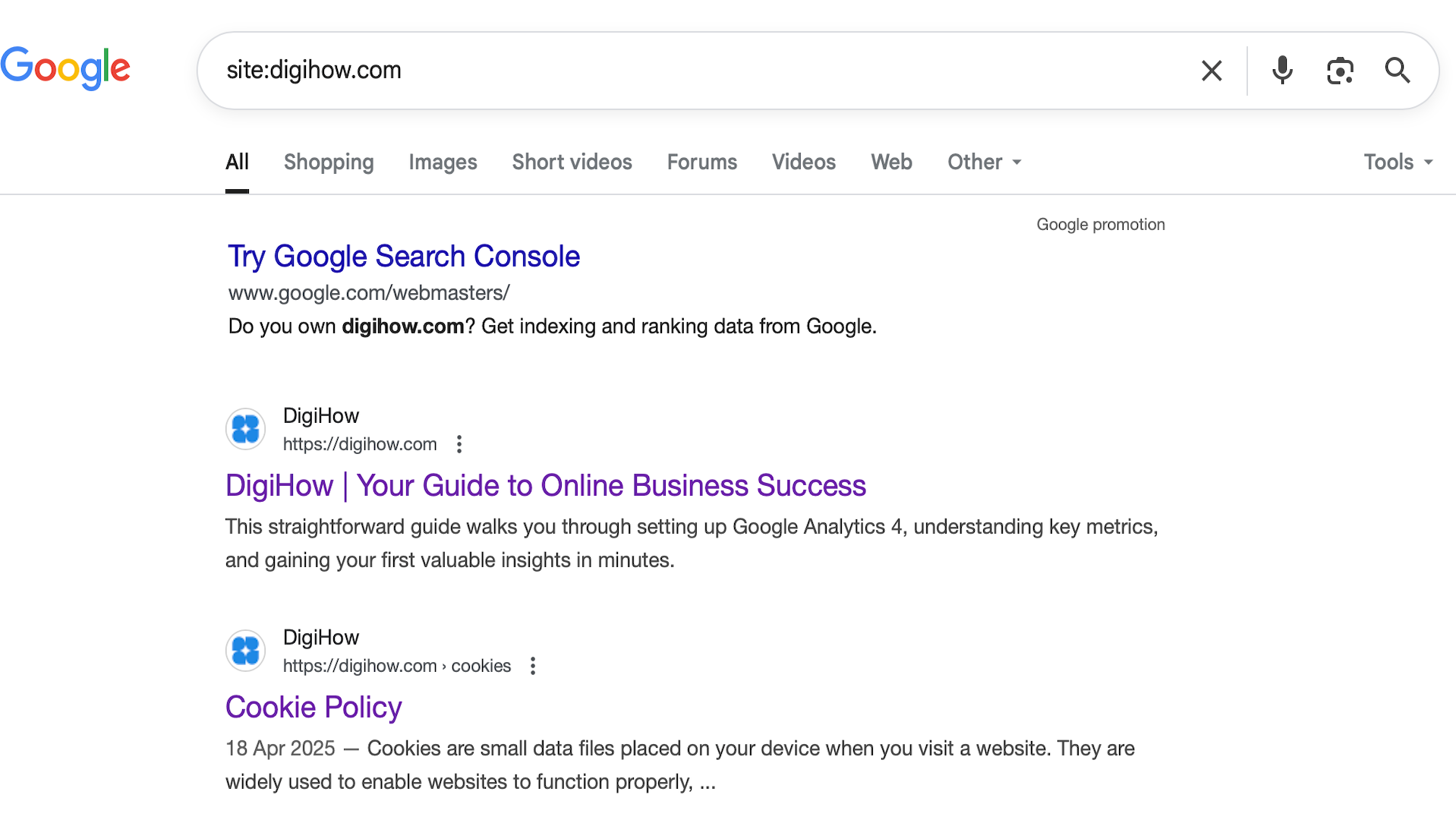
A Google Search of DigiHow using site:digihow.com
- Go to Google.com
- Type
site:yourwebsite.com(replace with your actual domain) - Hit Enter
On Bing
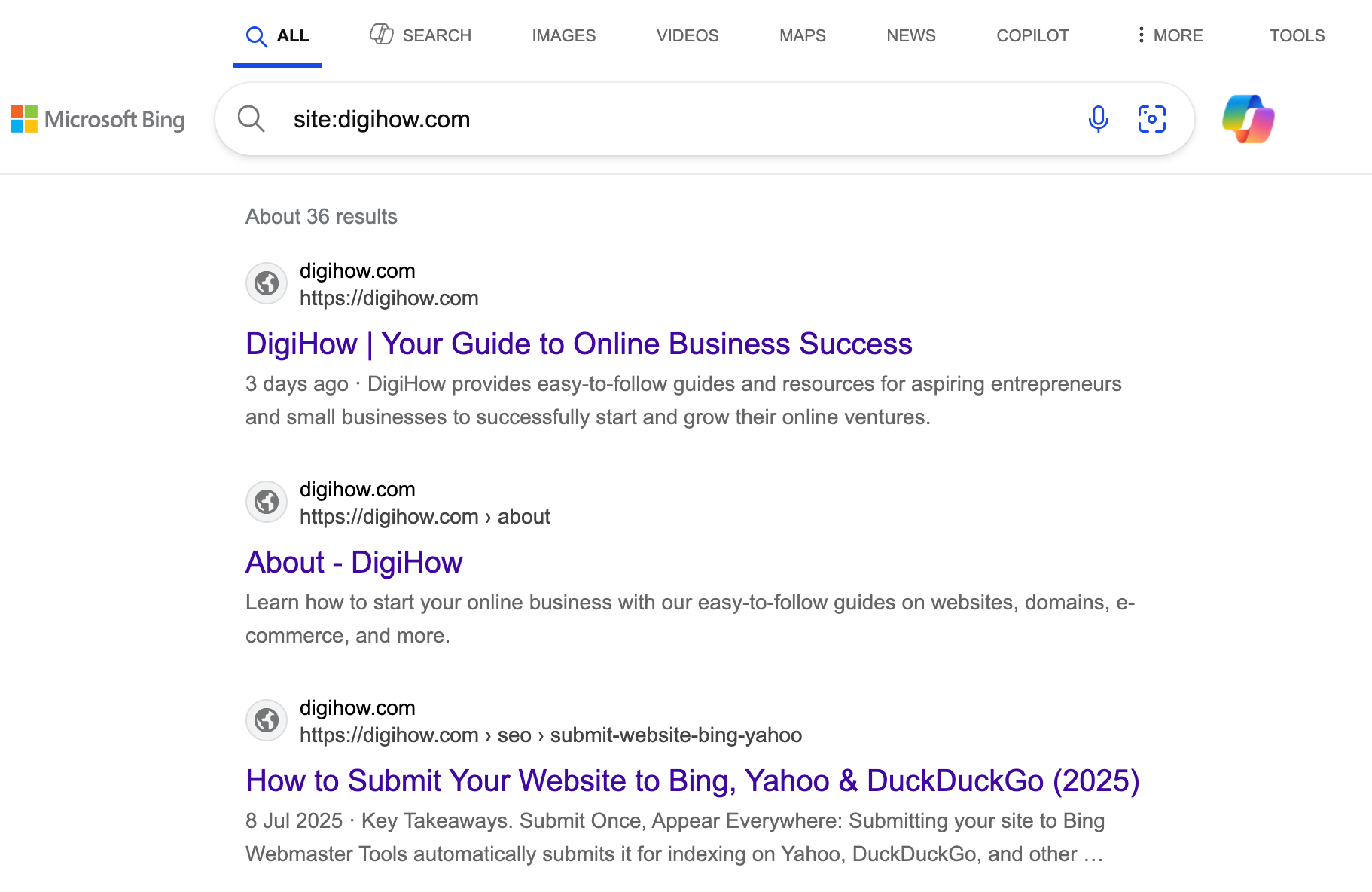
A Bing Search of DigiHow using site:digihow.com
- Go to Bing.com
- Type
site:yourwebsite.com(same format) - Hit Enter
Example searches:
site:digihow.comsite:yourstore.comsite:myblog.co.uk
What the Results Tell You
Good Signs
- Pages appear in results: Your site is indexed and discoverable
- Homepage shows up first: Usually indicates good site structure
- Recent content appears: Shows Google is crawling regularly
- Multiple pages listed: Indicates broader site indexing
Potential Issues
- No results at all: Your site might not be indexed yet
- Very few results: Only part of your site is indexed
- Old results only: Google hasn’t crawled recently
- Wrong pages ranking first: Possible site structure issues
What This Method Can’t Tell You
The site: operator is great for a quick check, but it has limitations:
- Not 100% accurate: May show slightly more or fewer pages than actually indexed
- No error details: Won’t tell you why pages aren’t indexed
- No traffic data: Can’t see which pages get clicks
- No indexing speed: Won’t show how fast new content gets indexed
- No mobile vs desktop: Doesn’t distinguish between mobile and desktop indexing
When to Use This Method
Perfect for:
- New websites (checking if Google found you)
- Quick competitor research
- Verifying a specific page is indexed:
site:yoursite.com "exact page title" - Checking after major site changes
Not ideal for:
- Ongoing SEO monitoring
- Understanding indexing problems
- Tracking search performance
- Finding technical issues
Advanced site: Operator Tricks
Check Specific Page Types
site:yoursite.com filetype:pdf- Find PDF filessite:yoursite.com inurl:blog- Pages with “blog” in URLsite:yoursite.com intitle:"contact"- Pages with “contact” in title
Exclude Certain Pages
site:yoursite.com -inurl:category- Exclude category pagessite:yoursite.com -filetype:pdf- Exclude PDF files
Check Competitors
site:competitor.com- See what pages they have indexedsite:competitor.com "keyword"- Find their content about specific topics
What to Do Based on Your Results
If You See No Results
- Wait if site is brand new (up to 4 weeks for new domains)
- Check your robots.txt file at yoursite.com/robots.txt
- Look for “noindex” tags in your page source
- Submit your website properly - our guides show you how to get your website on Google and how to submit your website to Bing and Yahoo
- Get links from other websites to help search engines discover you
If You See Some Results But Not All Pages
- Check internal linking - make sure pages link to each other
- Review page quality - thin content often doesn’t get indexed
- Look for duplicate content issues
- Verify pages load correctly and aren’t blocked
If Results Look Wrong
- Check page titles and descriptions match your content
- Review site structure and navigation
- Look for redirect issues
- Consider technical SEO audit
Google vs Bing: What’s the Difference?
Both search engines use the same site: syntax, but you might see different results:
Google typically shows:
- More pages indexed
- Faster discovery of new content
- More frequent updates
Bing might show:
- Fewer total pages
- Different page prioritization
- Sometimes older content
Why check both:
- Bing powers about 20% of searches
- Different algorithms may catch different issues
- Provides broader perspective on your site’s visibility
Moving Beyond the Basic Check
While the site: operator gives you a quick snapshot of your indexed pages, it’s just the starting point for proper website visibility.
Next steps for complete search engine coverage:
-
Proper submission process - If your site isn’t showing up, follow our step-by-step guides for submitting to Google and submitting to Bing and Yahoo
-
Ongoing monitoring - For comprehensive indexing analysis, including understanding why pages aren’t indexed, tracking indexing speed, and identifying technical issues, you’ll need Google Search Console. Our detailed guide on Google Search Console errors shows you how to interpret the data that really matters and which “errors” you can safely ignore.
The site: search is perfect for quick checks, but proper submission and Search Console monitoring are essential for ongoing SEO success.
Quick Reference Checklist
Weekly Quick Check:
-
site:yoursite.comon Google -
site:yoursite.comon Bing - Note any significant changes in results
- Check if new content appears
Monthly Deep Dive:
- Review Google Search Console data
- Check for indexing trends
- Monitor site performance
- Address any technical issues
Red Flags to Investigate:
- Sudden drop in indexed pages
- Important pages not appearing
- Only homepage showing in results
- Very old content ranking first
The Bottom Line
The site: operator is your fastest way to check if Google and Bing can find your website. It’s not perfect, but it gives you immediate insight into your site’s basic visibility.
Use it for quick checks and competitor research, but don’t rely on it for detailed SEO monitoring. For that, you’ll need proper tools and regular analysis.
Most importantly, remember that being indexed is just the first step. The real goal is ranking well for searches your customers actually make - and that requires a more comprehensive approach to SEO.
Frequently Asked Questions
How accurate is the site: operator for checking indexing?
The site: operator gives a good general overview but isn’t 100% precise. It may show slightly more or fewer pages than actually indexed. For exact indexing data, use Google Search Console, but the site: operator is perfect for quick checks.
Why do I see different results on Google vs Bing?
Google and Bing use different algorithms and crawling patterns. Google typically indexes more pages and discovers new content faster, while Bing might show fewer pages or prioritize different content. Both results are normal.
What does it mean if I see no results at all?
No results usually means your site isn’t indexed yet. This is normal for new websites (can take up to 4 weeks). Check your robots.txt file, look for noindex tags, and consider submitting your site properly to search engines.
Can I use site: to check specific pages?
Yes! Use site:yoursite.com “exact page title” to check if specific pages are indexed. You can also use site:yoursite.com inurl:blog to find pages with “blog” in the URL, or other variations.
Should I be worried if I see very few results?
Not necessarily. If your important pages appear and you’re getting traffic, you’re fine. Many “missing” pages might be ones you don’t want indexed anyway, like admin pages, thank you pages, or duplicate content.